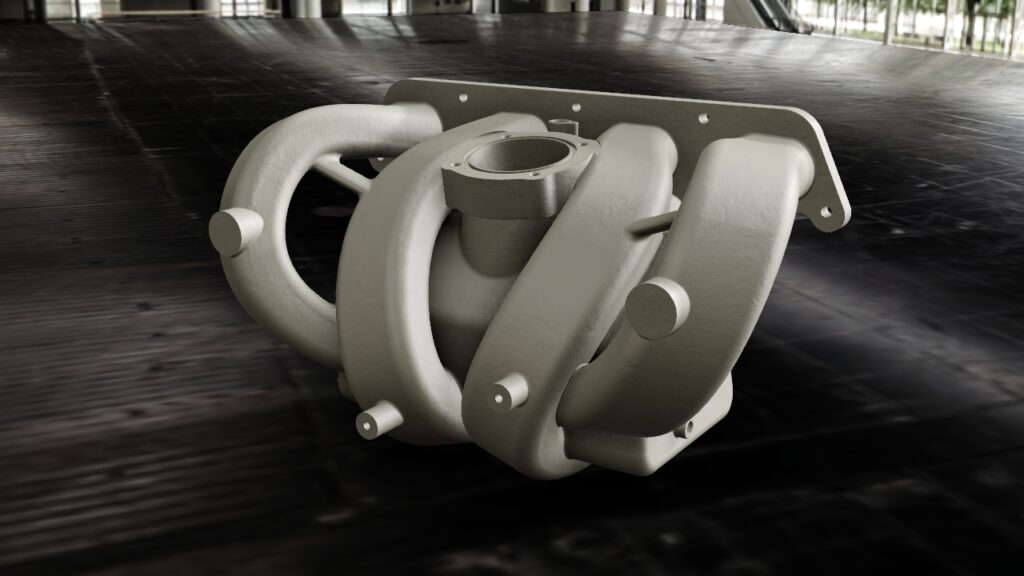
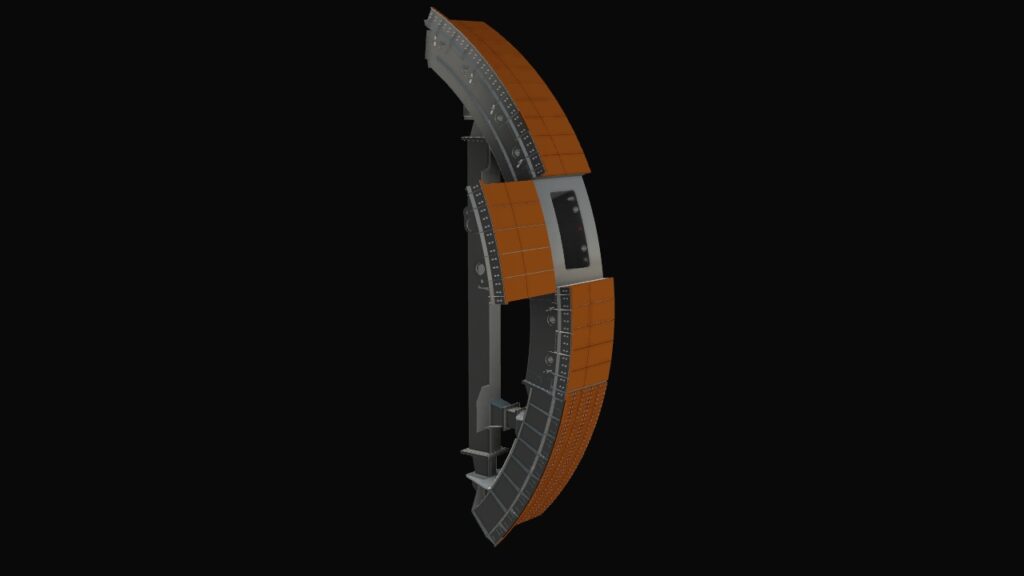
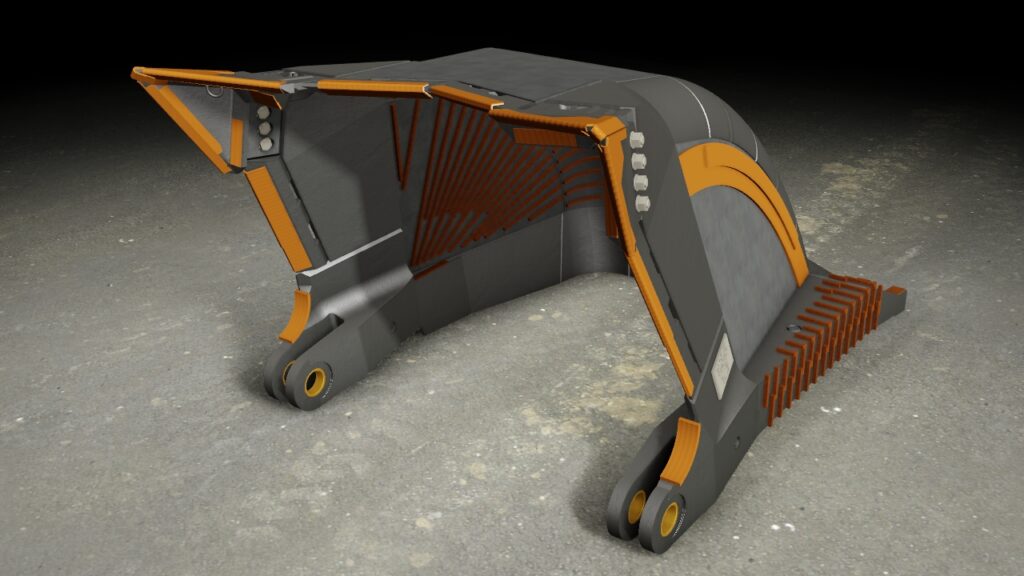
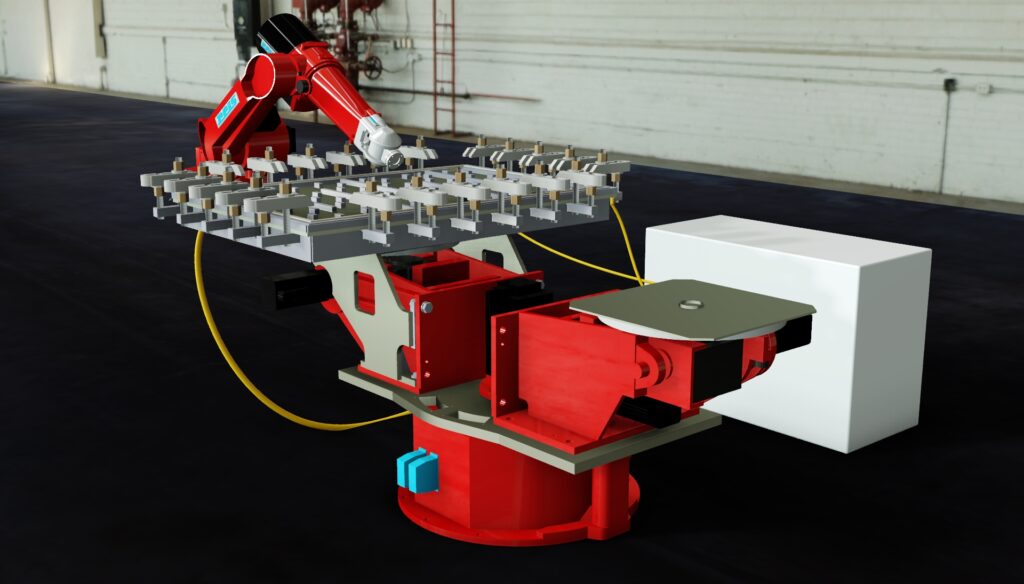
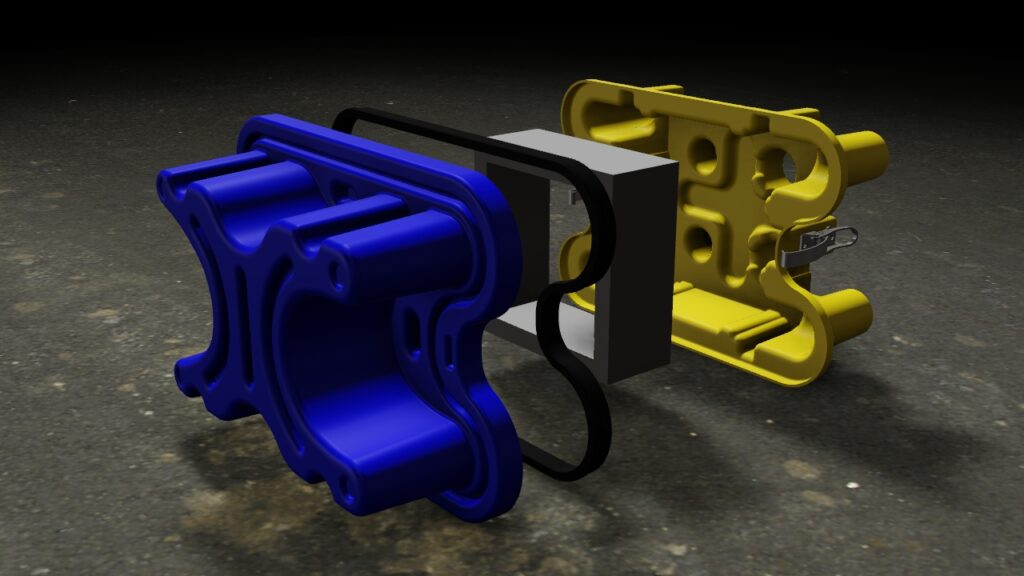
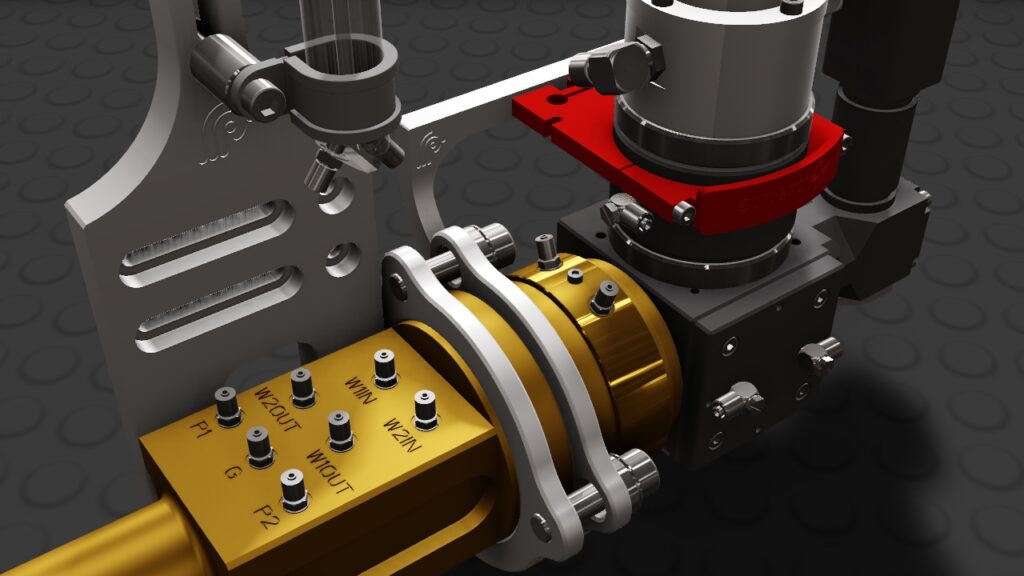
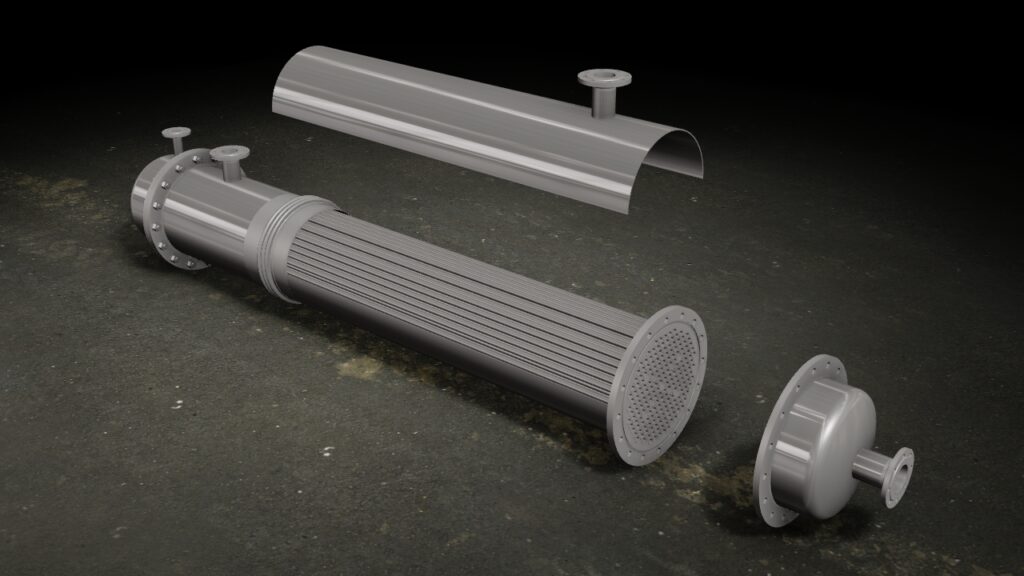
Our CAD service includes 3D CAD design in particular. 3D laser scanning expands and complements our 3D CAD service. We have more than 35 years of experience in the field of 3D CAD design of combustion engines, dynamic steel construction, plant engineering, industrial goods and plastic parts. We model both complex assemblies and sophisticated free-form surfaces with C2 continuous transitions. By using the latest 3D CAD systems, product developments can be carried out much faster and more economically than with conventional 2D systems.
Advantages of modern CAD design:
– Creation of parametric, complex volume and surface models
– Package investigations, installation space optimization
– Structural optimization with associatively communicating 3D model and FEM tool
– Sheet metal part construction with automatic derivation of the sheet metal part development
– Variant construction based on parametric CAD data
– Assembly simulation, collision control
– Kinematic motion analysis
– Visualization, animated assemblies, photorealistic representation, exploded view
– Drawing derivation bidirectionally associative to the 3D data
– Output of all common neutral CAD formats (STEP, IGES, STL, SAT, VDA, DXF, DWG)