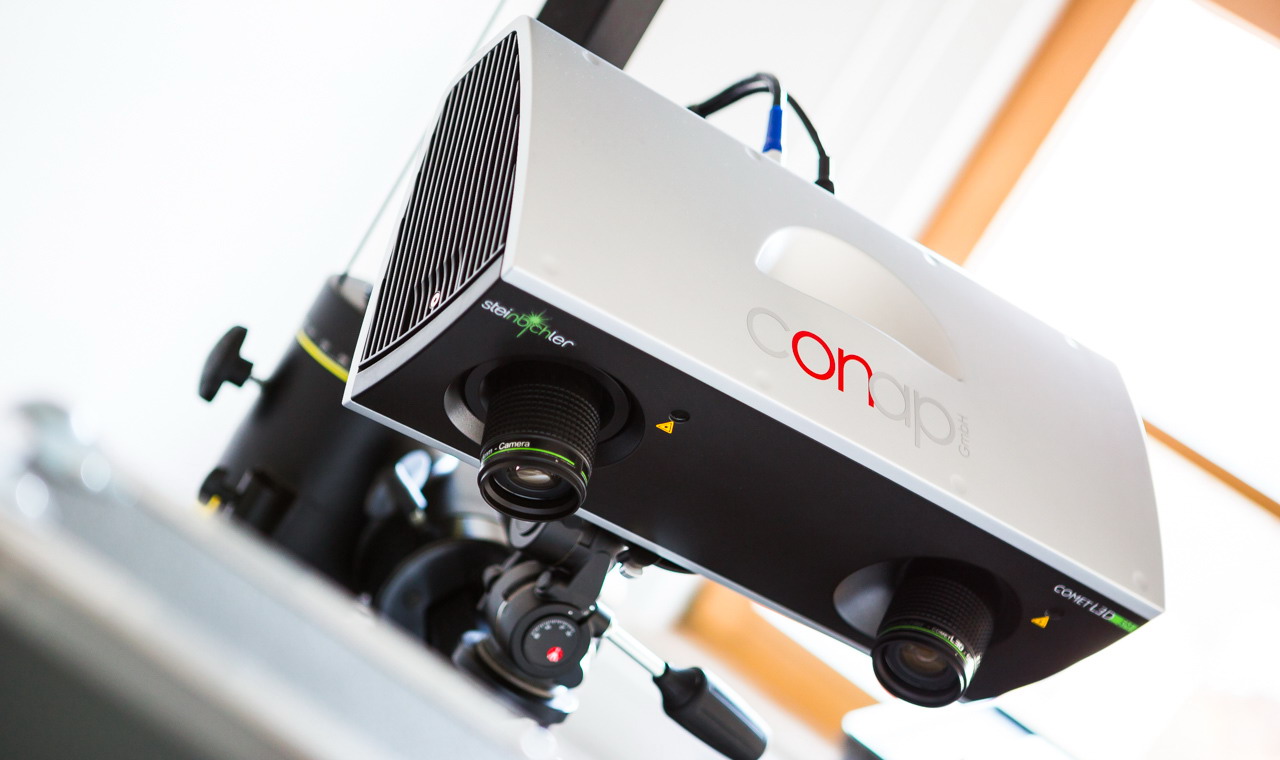
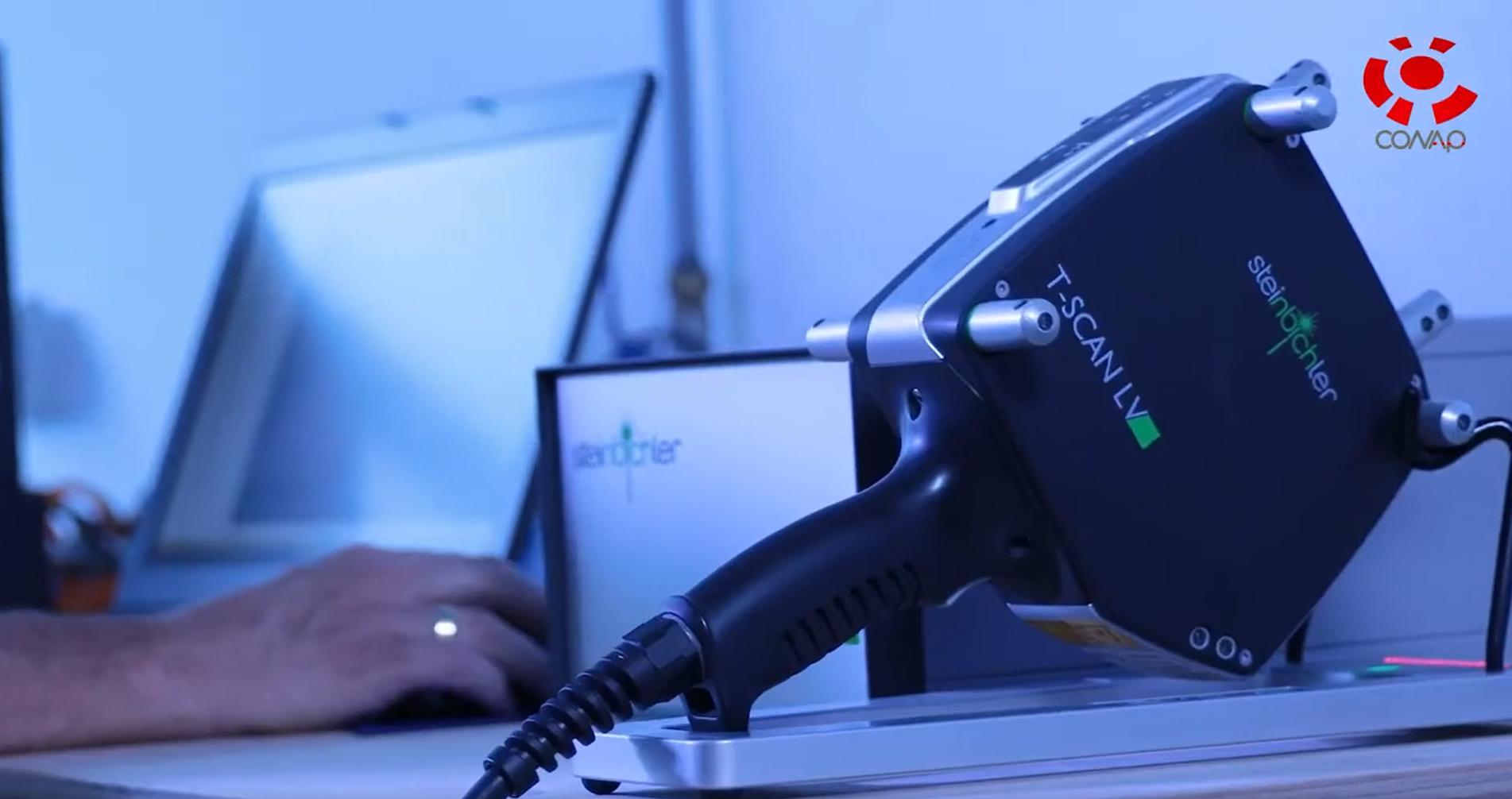
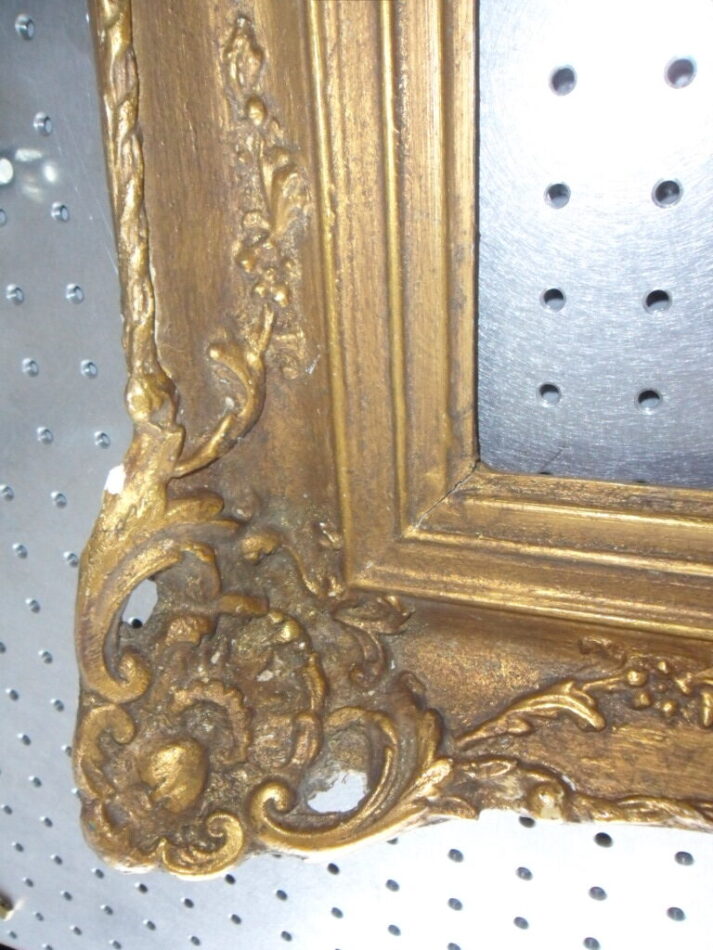
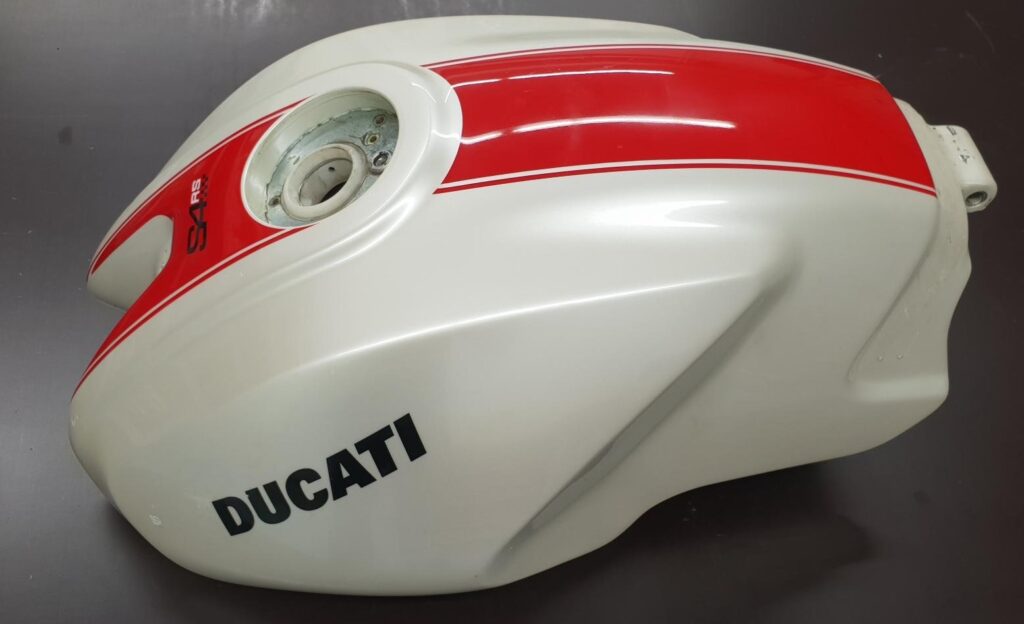
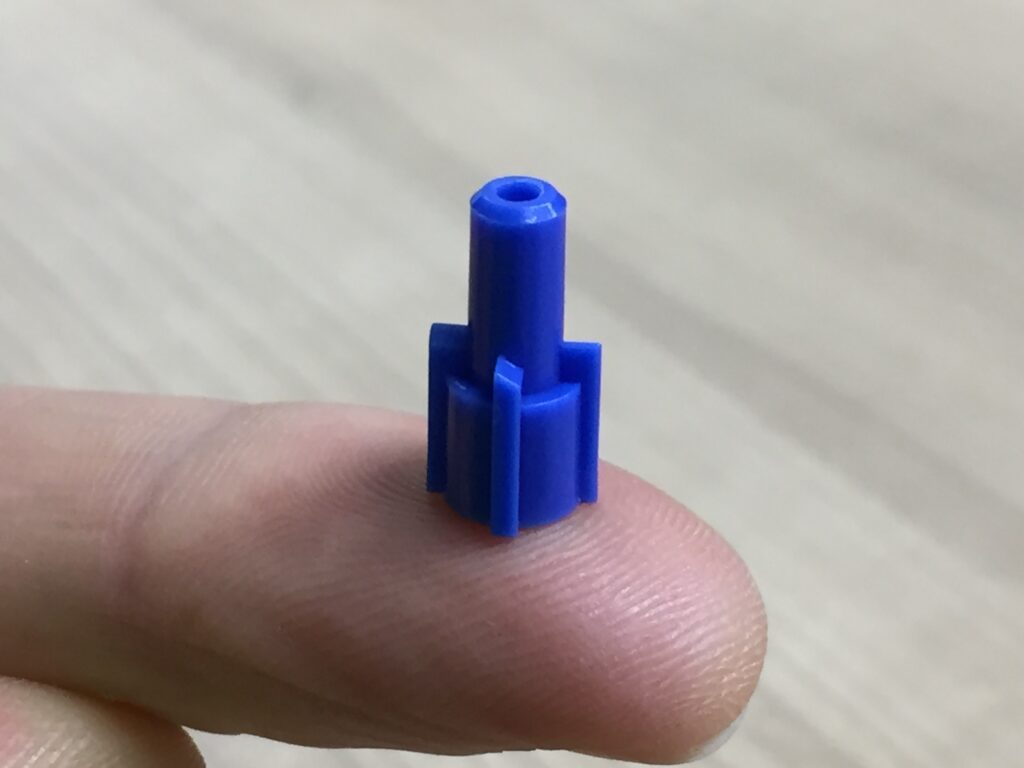
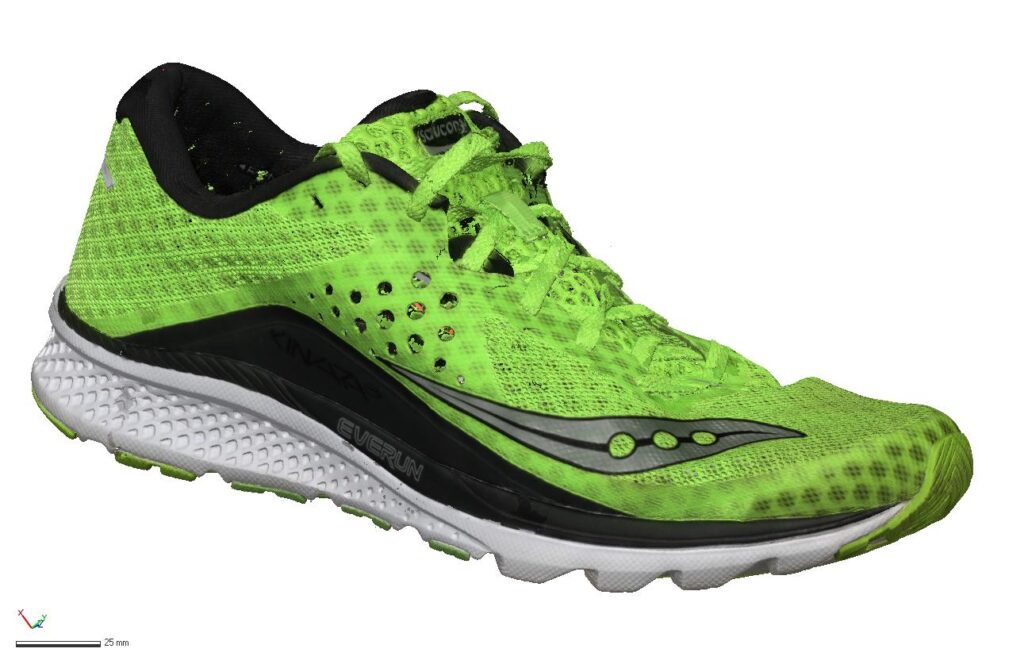
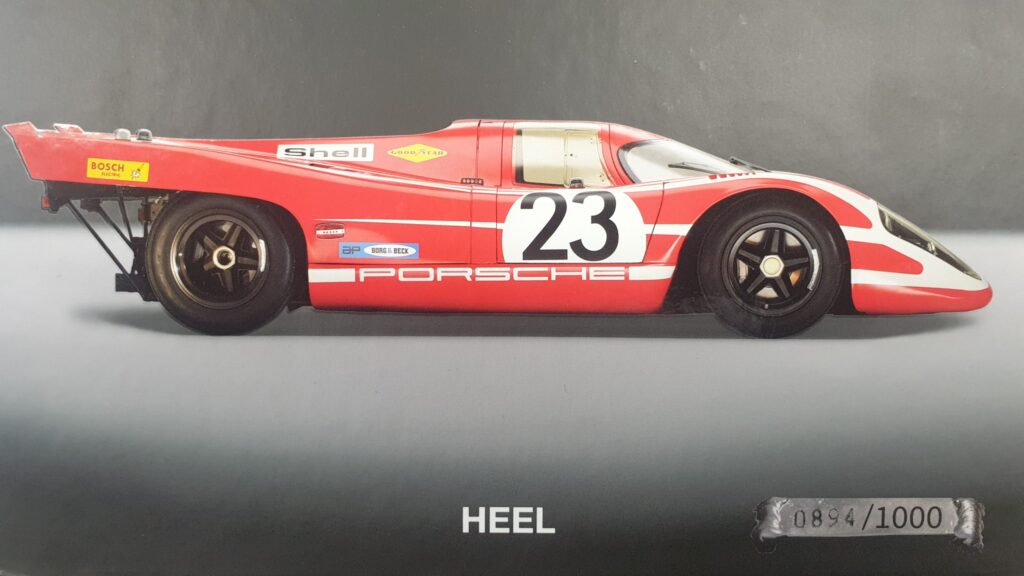
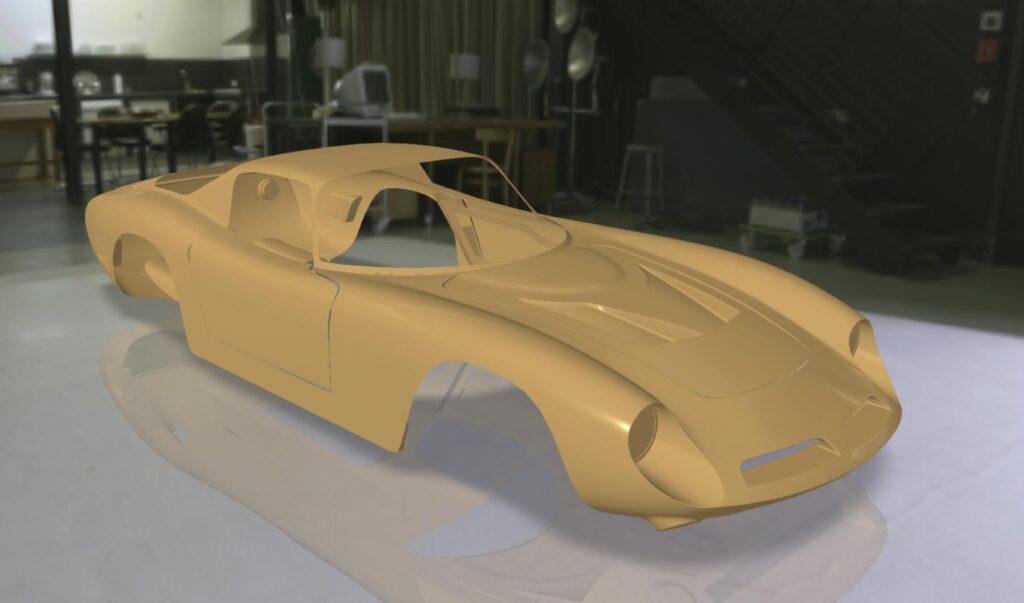
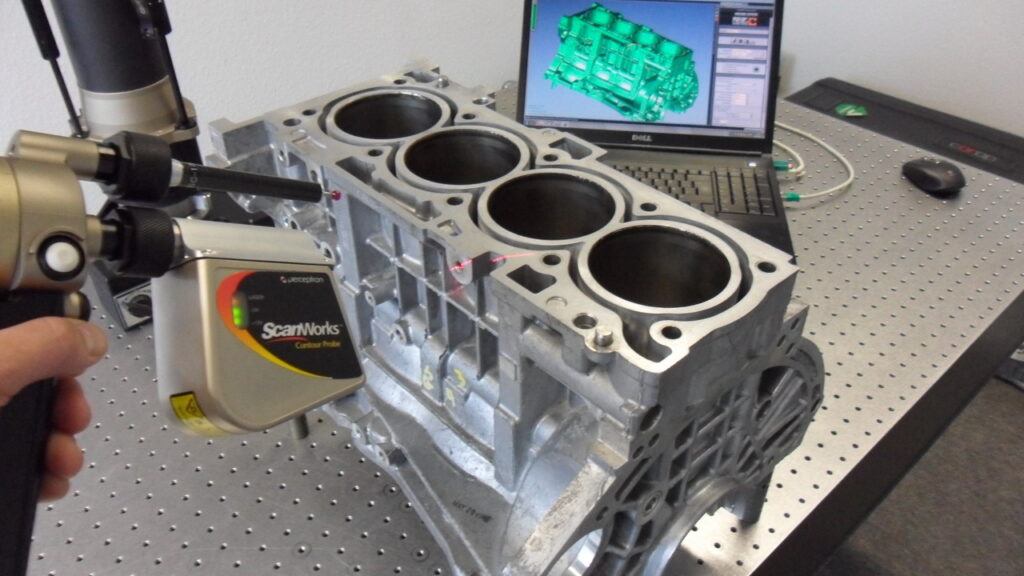
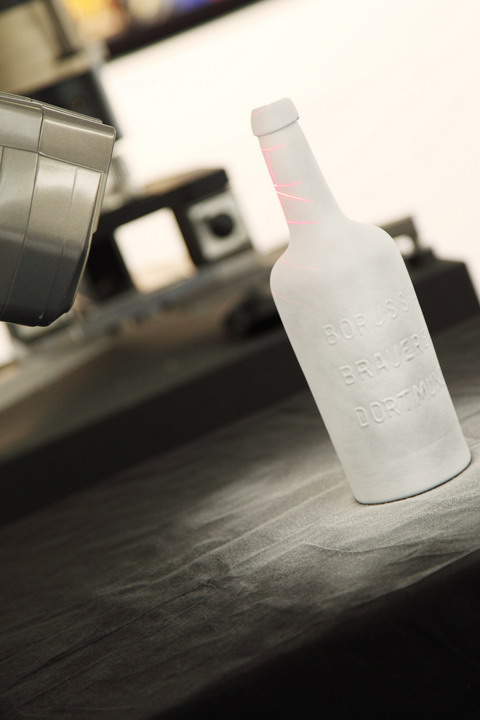
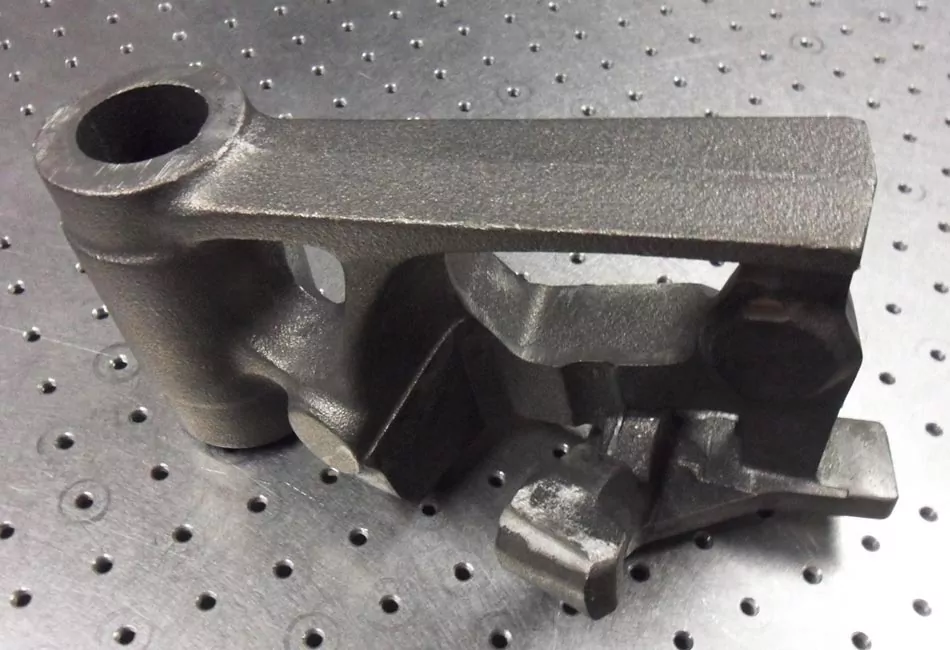
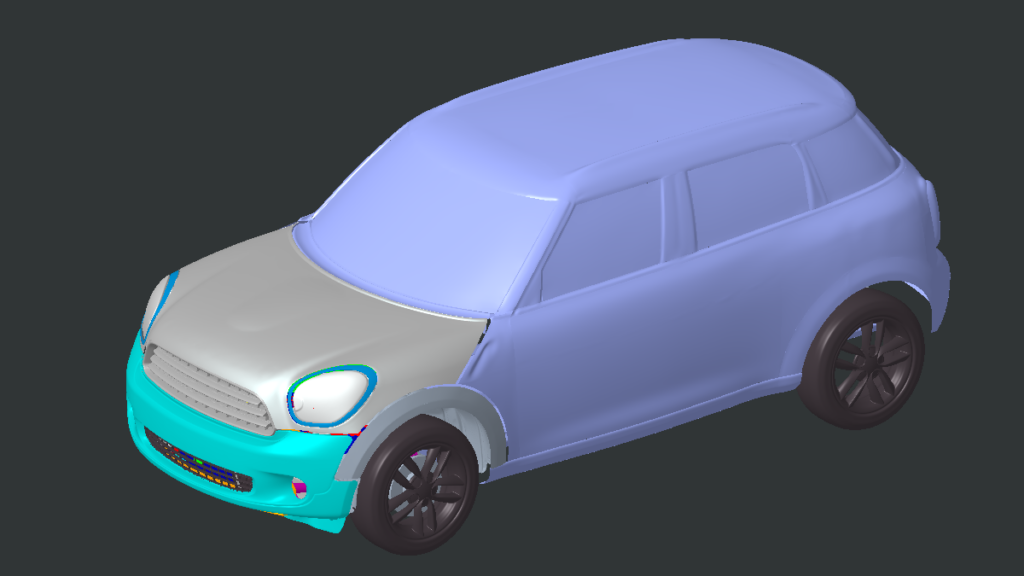
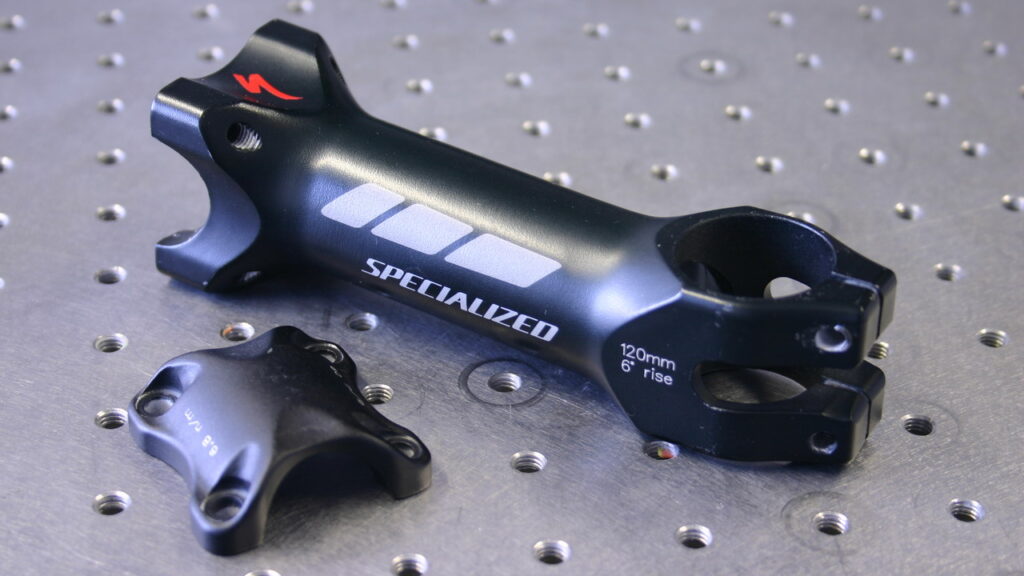
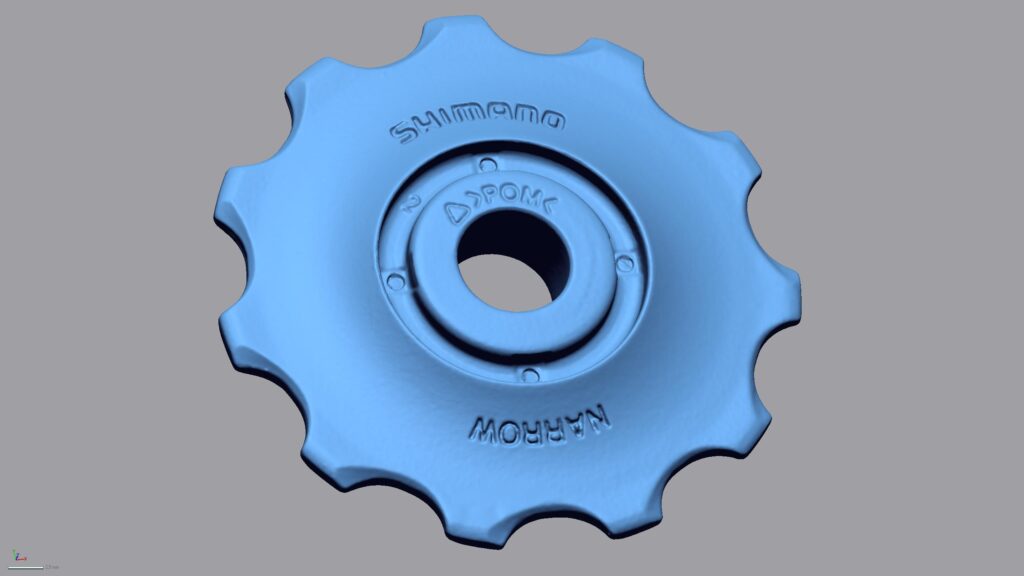
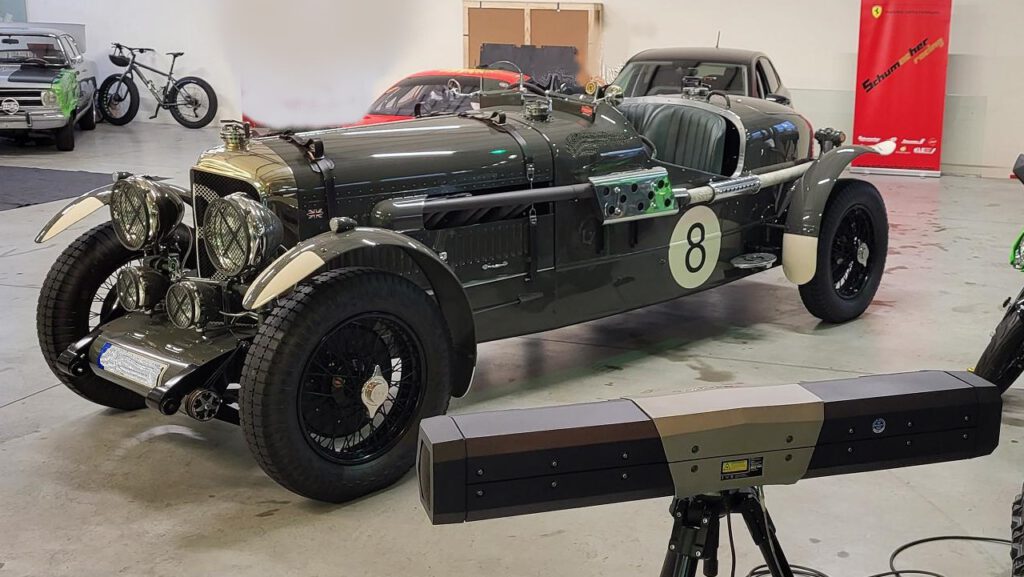
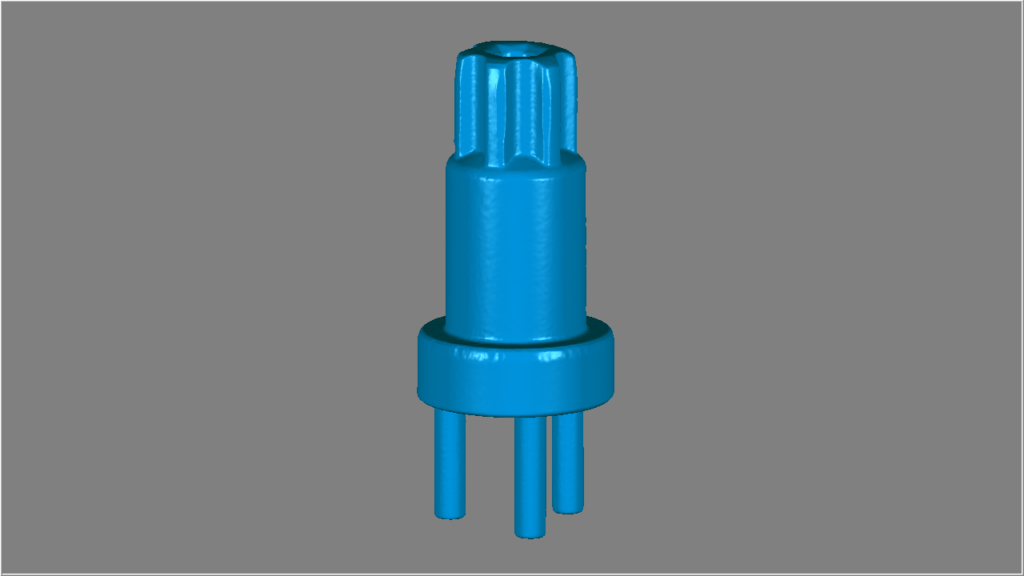
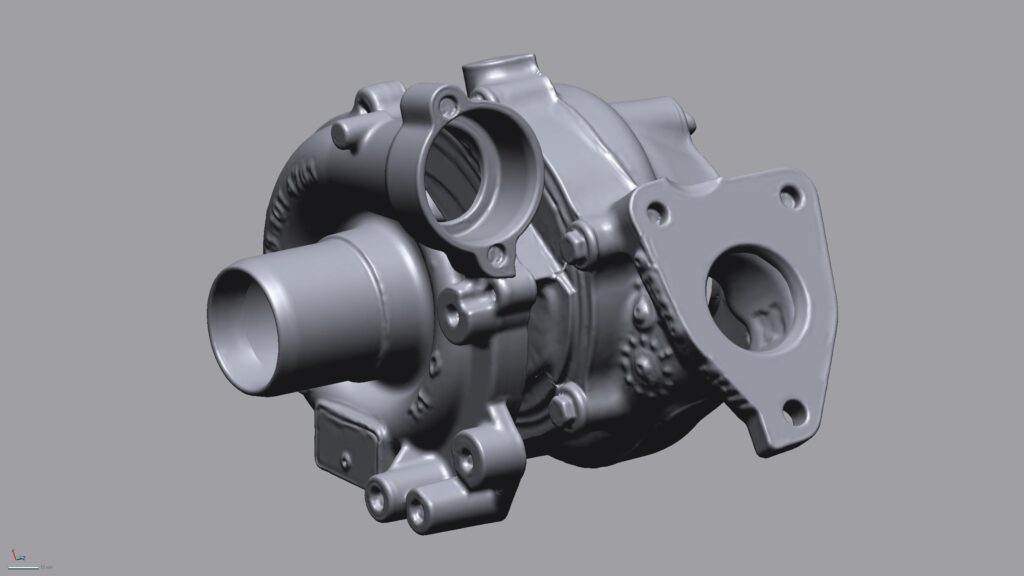
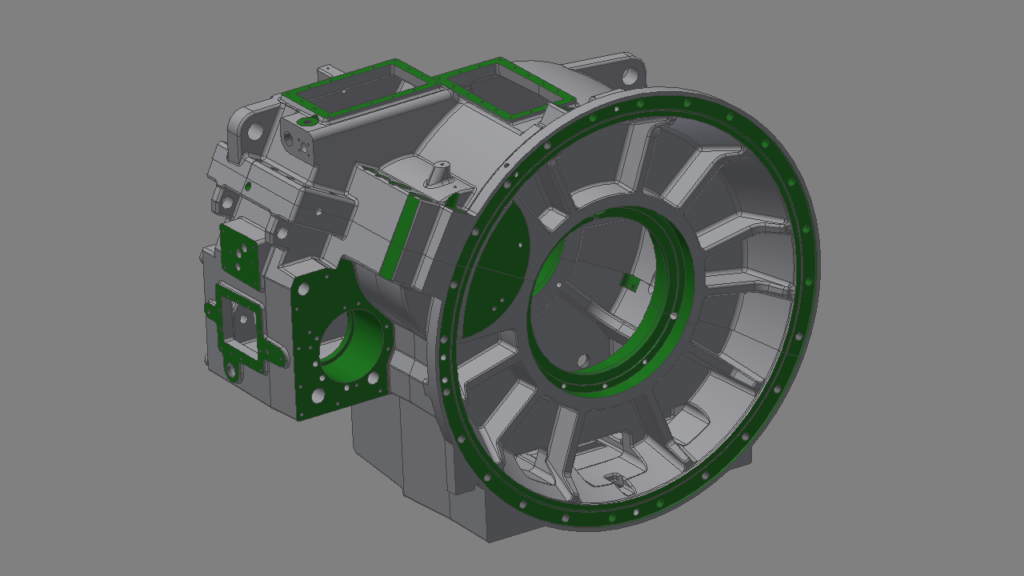
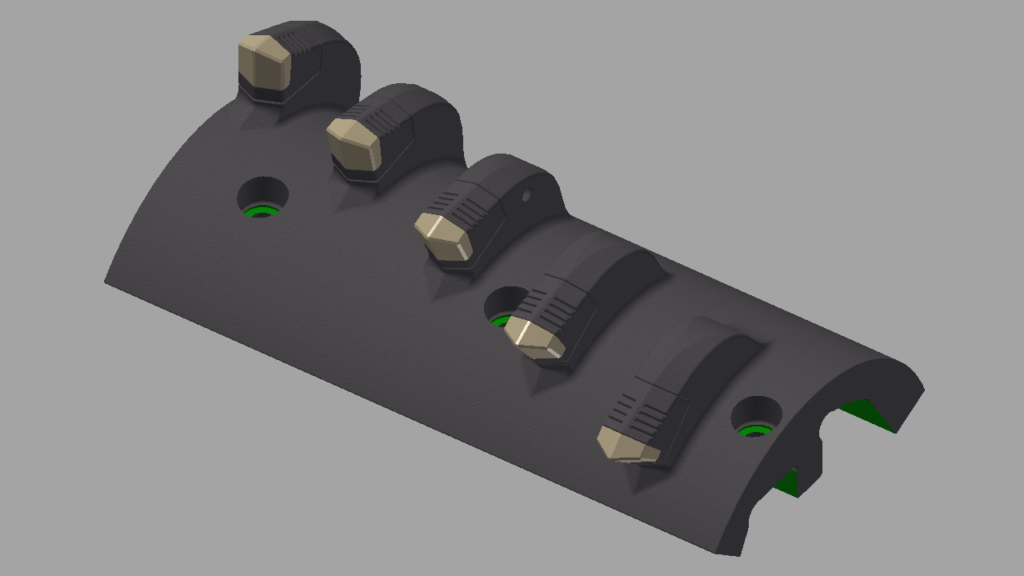
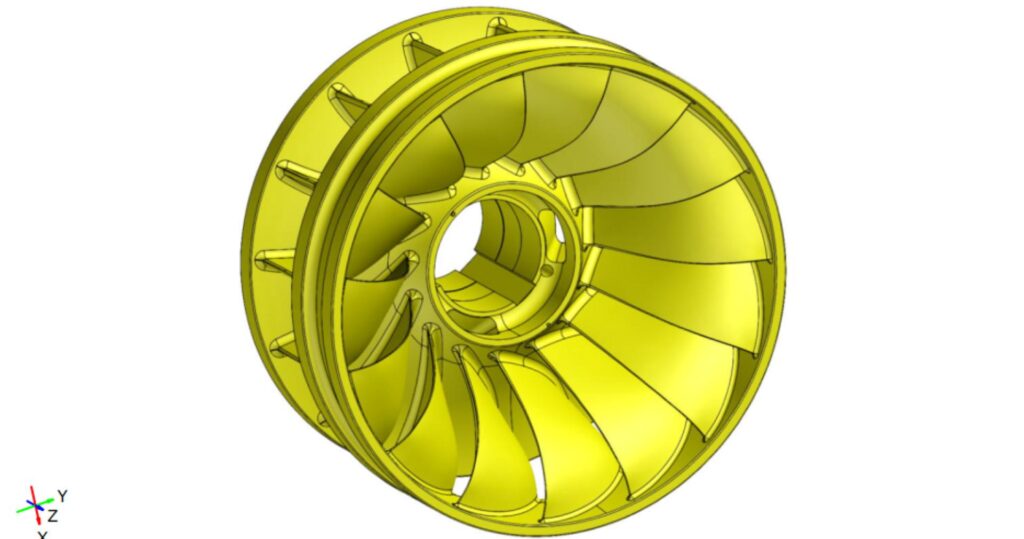
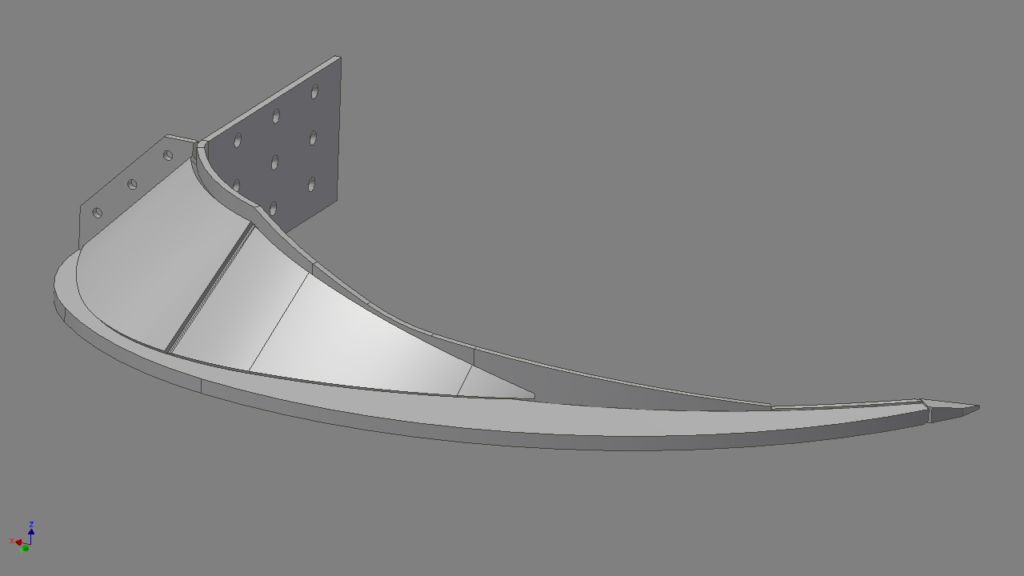
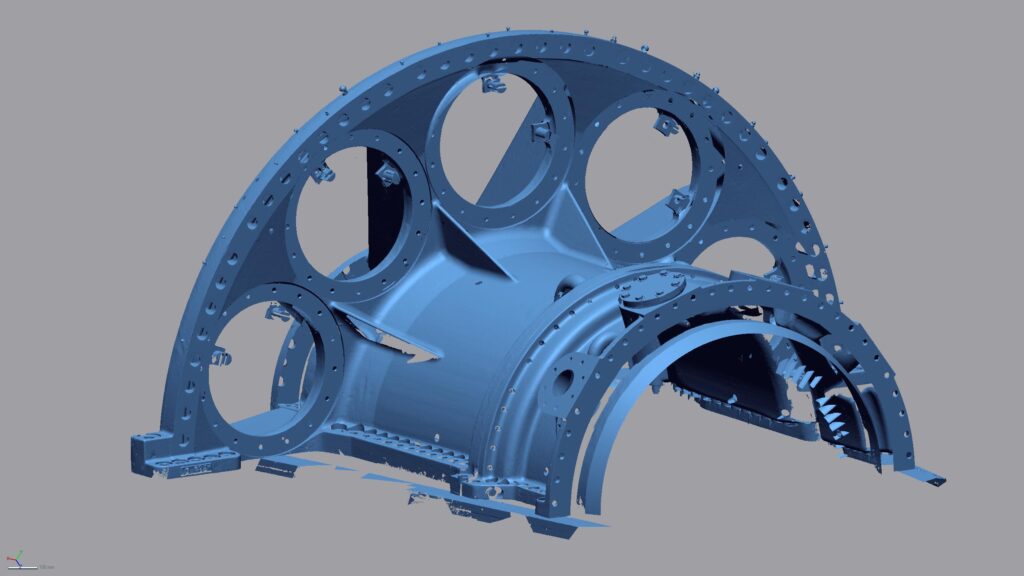
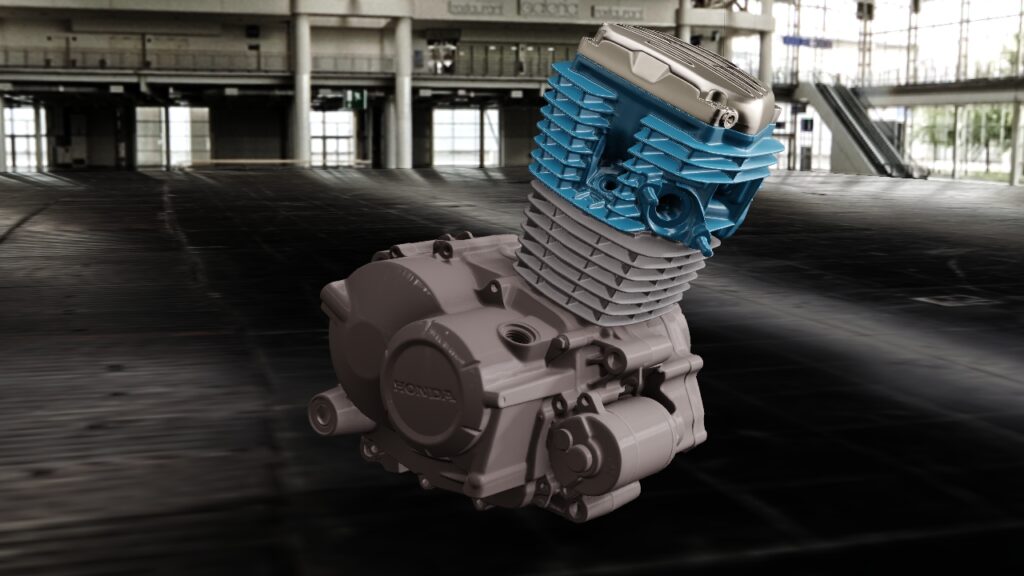
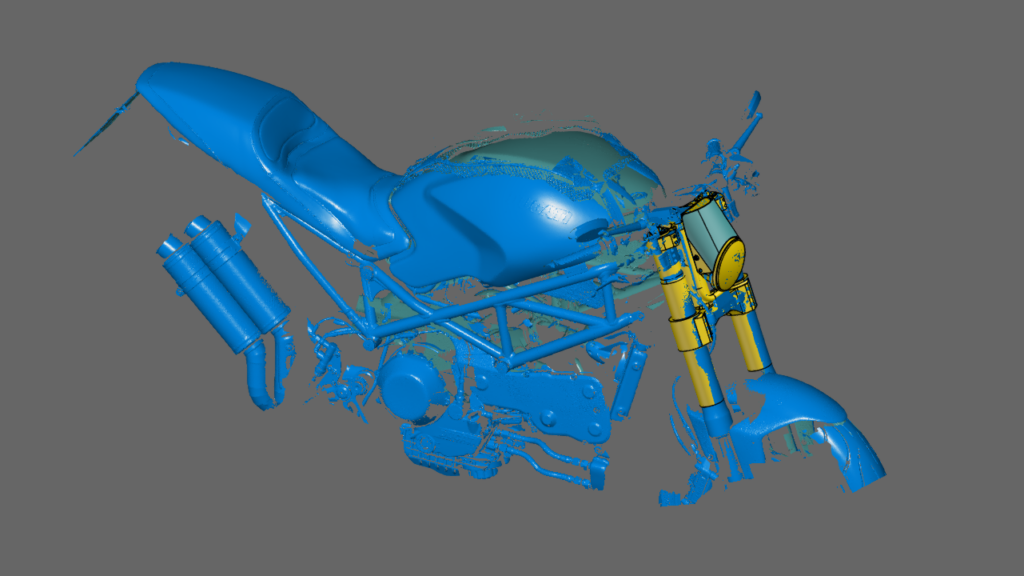
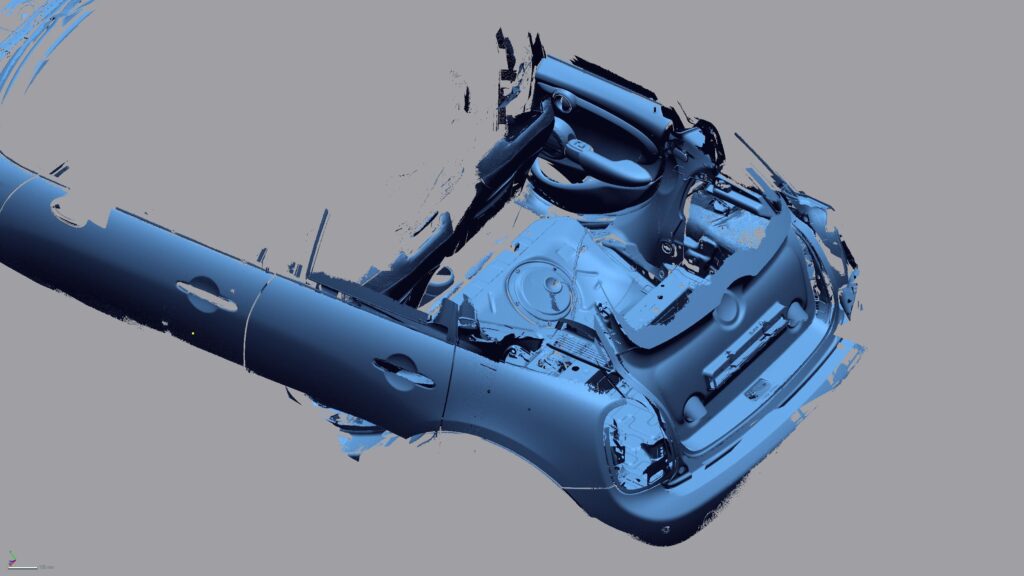
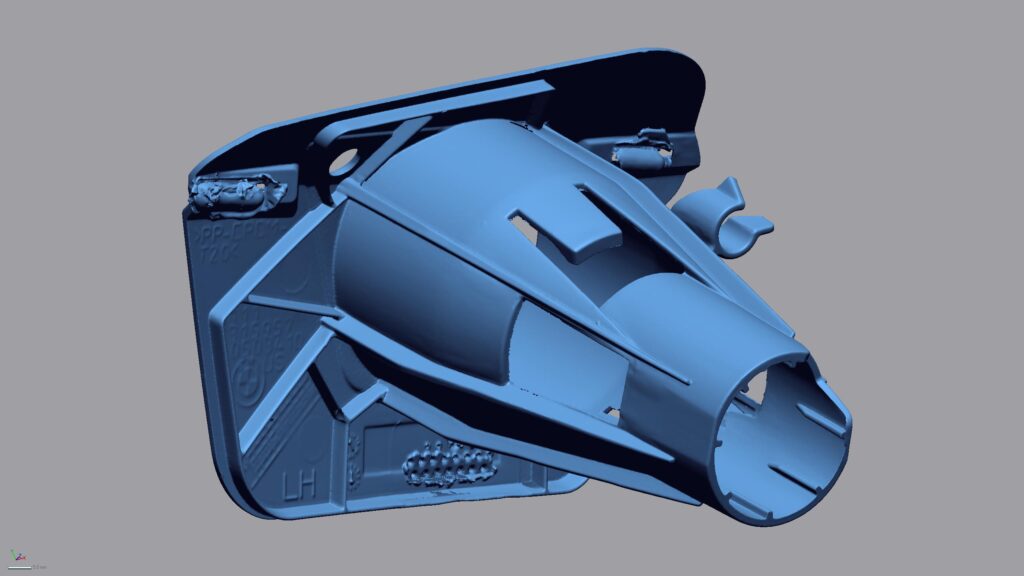
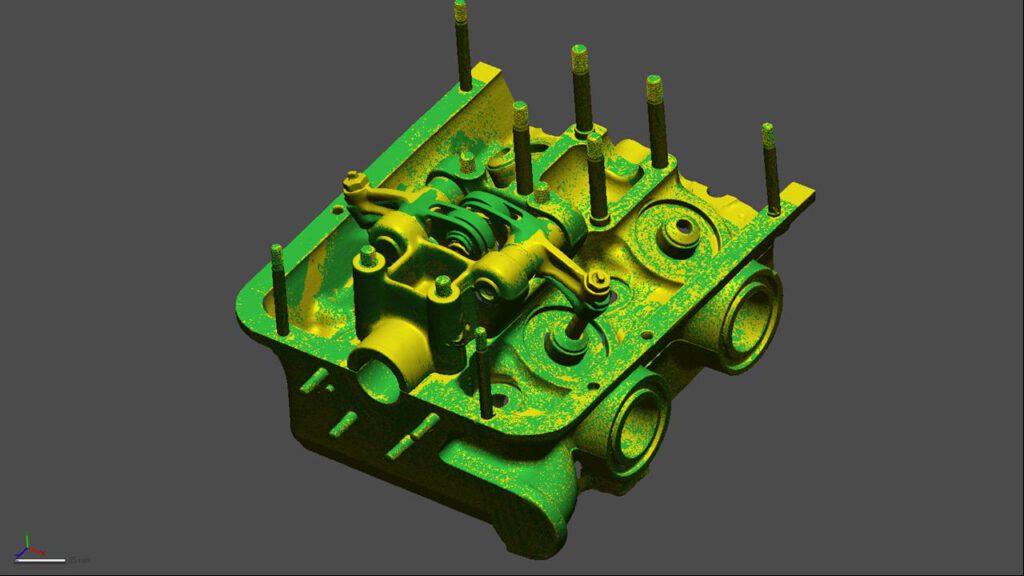
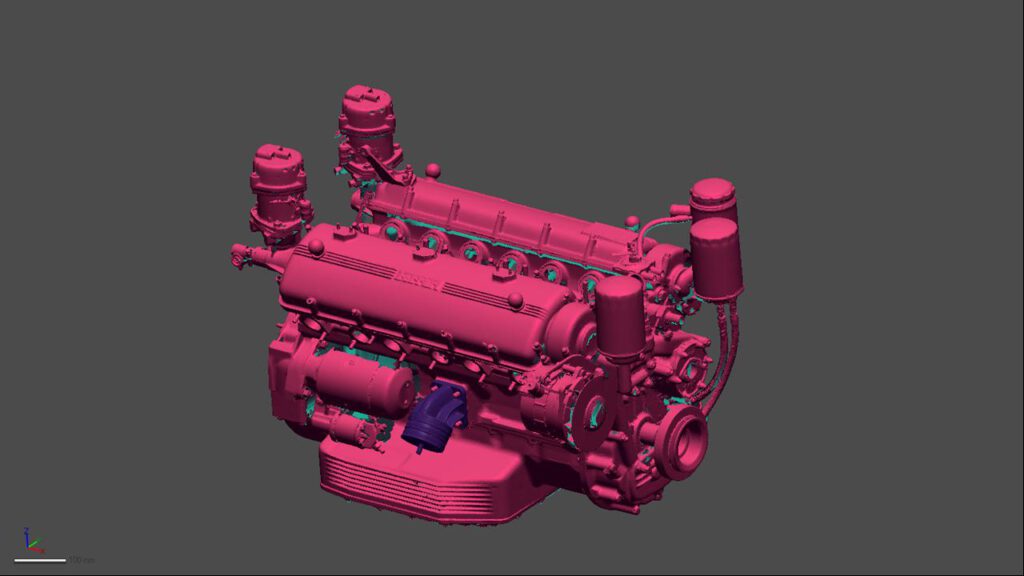
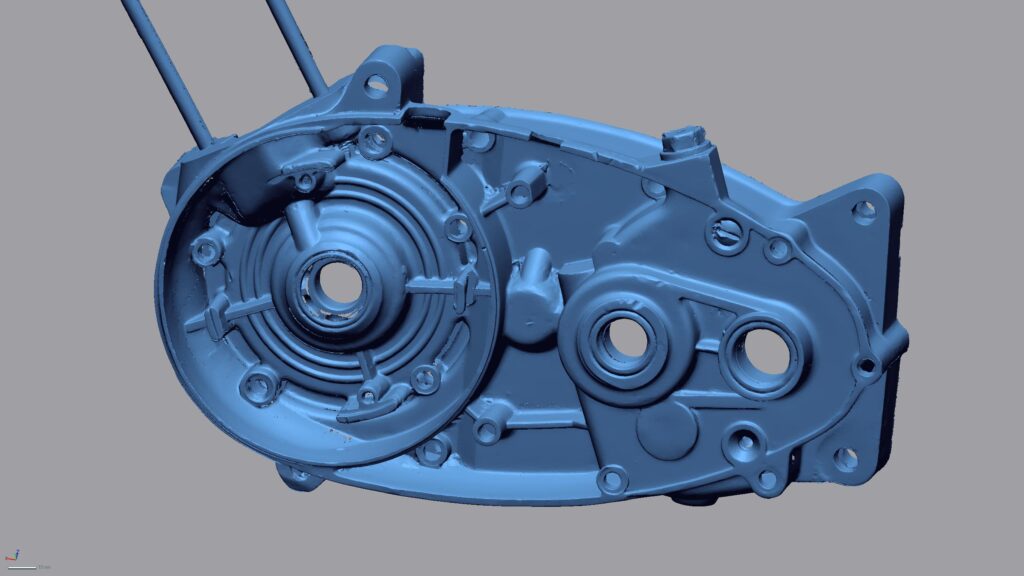
With our 3D scanning service, your object is created as an extremely detailed digital data model
Would you like to digitize any object in 3D for which no 3D CAD data is available?
Our 3D scanning service even enables the digitization of objects that are otherwise difficult to capture, large or small. conap uses 3D scanners to scan objects of any shape without contact. This involves recording several million points that are combined to form a 3D point cloud, creating an extremely detailed digital data model of the entire physical object. The basic geometric information of the object being measured is millions of times greater than with conventional tactile measuring techniques.